In the previous tutorials, we showed you how to create EMF models by importing Rose models or annotated Java interfaces. This may have seemed like a somewhat indirect way of creating a model in EMF. In this tutorial, we will show you how to create the Library model from scratch using a graphical editor that manipulates the EMF model directly. An EMF model file has the extension .ecore and therefore sometimes referred to as an ecore model.
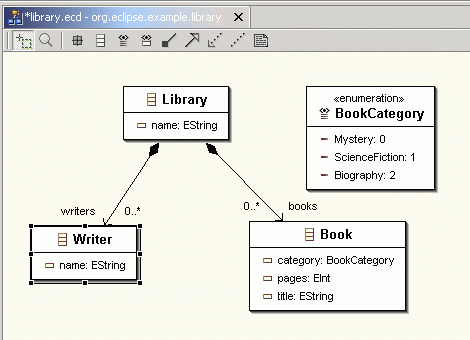
The graphical editor is provided by Omondo through their EclipseUML plugin. The following is the class diagram of the Library model we dealt with in the first tutorial shown in Omondo graphics and icons.
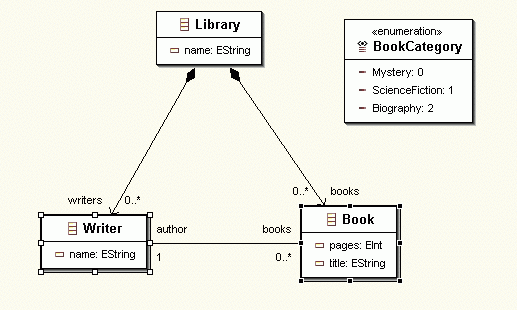
The screenshots in this tutorial were captured using version 2.1 of the Eclipse SDK, version 1.1.0 (build 20030519_0521VL) of EMF, version 2.1.0 of GEF, and version 1.2.1 of EclipseUML.
Contents
| Step 0: | Prerequisites |
| Step 1: | Creating a New Model |
| Step 2: | Creating Classes |
| Step 3: | Creating Associations |
| Step 4: | Generating the Model and Editor |
| Step 5: |
Modifying the Model |
Step 0: Prerequisites
Download and install the latest EclipseUML plugin from the Omondo web site (http://www.omondo.com/) and its dependent plugins. The screenshots below were captured when version 1.2.1 was available, but you should use the latest version you find on the Omondo web site.
- Download the Auto-Installer and save the jar file in, say, c:\temp.

(If you already have the GEF and EMF plugins, you might want to download the zip file which is smaller, but make sure you have the correct versions of the dependencies.)
- Execute the jar file you downloaded:
C:\> cd c:\temp
C:\temp> java -jar eclipseuml-installer_1.2.1.ar
- Follow the instructions as the installer runs to install the EclipseUML, GEF, and EMF plugins into your Eclipse installation.
- Launch Eclipse. If you have run Eclipse before installing EclipseUML, you will be prompted to run the Update Manager. Select Yes and follow through the steps to install EclipseUML.
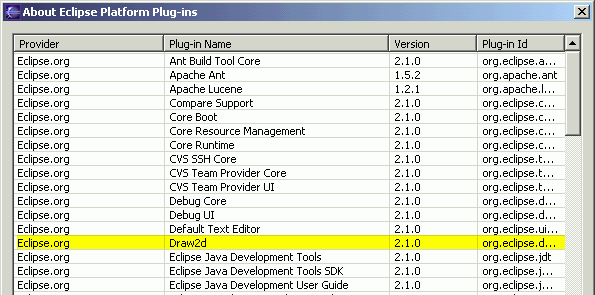
Select Help>About Eclipse Platform.

- Click the Plug-in Details button.

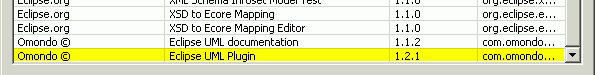
- Verify that the following highlighted plugins show up in the dialog.

Step 1: Creating a New Model
We first create a Java project and then use the wizard to create a new EMF model.
- In the Navigator view in the Resource perspective, right-click on the blank area and select New > Project...:

- Select "Java" and "Java Project". Click the "Next" button.

- Enter library as the project name. Click the Finish button.
- Click the "Add Folder" button.
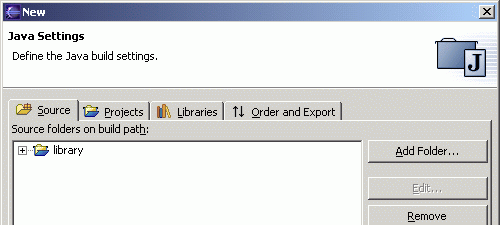
- Click the "Create New Folder" button.
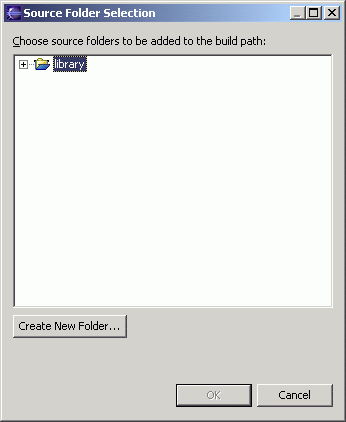
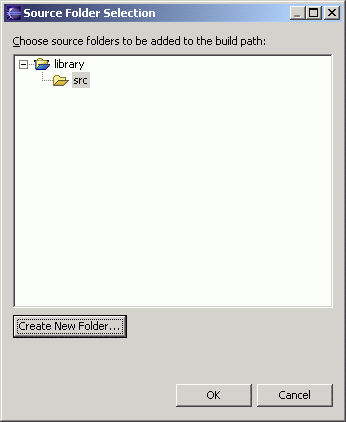
- Type "src" and click the "OK" button.

- Click the "OK" button.
- When asked if you want to remove the project as source folder and update the build output folder to "library/bin", click the "Yes" button.
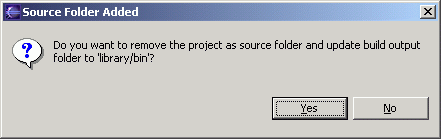
- Specify "library/runtime" as the build default output folder. Click the "Finish" button.
- The newly created Java project can be seen in the Package Explorer.
- On the Navigator view, right-click on the src folder and select New > Folder.

- Enter model as the folder name. Click the Finish button.

- With the model folder selected, select File > New > Other....

- Select EMF Diagrams on the left pane and EMF Class Diagram on the right. Click the Next button.

- Change the file name to library.ecd and the package name to org.ecilpse.example.library. You can also add some description if your like. Click the Finish button.
- A pair of files, the .ecore and the .ecd files, will be created and the graphical editor will be opened in the main view.

The .ecore file contains the structure of the model while the .ecd file contains the graphical layout information.
Step 2: Creating Classes
- In the editor view, click on the Create a class button, and then click anywhere in the blank area. A New Class dialog will come up.

- Enter Library as the class name. Click the Finish button.
- A Library class will be drawn in the main view. You can drag it around and place it wherever you prefer.
Now, right-click on it and select New > Attribute.

- Enter name as the name of the attribute. Ensure that the other properties match what is shown below. Click the OK button.

- You have just created a class named Library with a String attribute named name.

- There is also another way of creating classes. First, you click in the blank area of the editor to deselect any class you might have selected. Then, right-click in the blank area of the main view and select New > Class.

- Enter Writer as the class name and click the Finish button.

- Create the name attribute for the Writer class just like before. Right-click on Writer, select New > Attribute, then enter name for Name and click the OK button.

- Now we are going to create an enumeration class. You can click on the
 button and then anywhere on the blank area, or right-click on the blank area and select New > Enumeration to bring up the New Enumeration dialog. Enter BookCategory as the name of the enumeration.
button and then anywhere on the blank area, or right-click on the blank area and select New > Enumeration to bring up the New Enumeration dialog. Enter BookCategory as the name of the enumeration.

- For each of the three literals shown below, click on the Add... button, enter the name and value of the literals, and then click the OK button.
Name
Value
Mystery
0
ScienceFiction
1
Biography
2

- At this point, the New Enumeration dialog should appear as shown below. Click the Finish button.
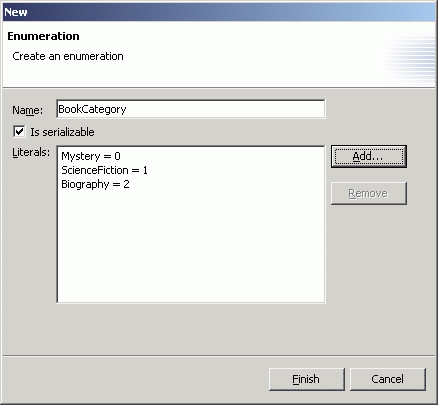
- The BookCategory enumeration is created and shown in the editor.

- We are now going to create the Book class. Right-click on the blank area and select New > Class. Enter Book as the class name and click the Finish button. Then, with the Book class selected, right-click and select New > Attribute, enter title as the attribute name and click the OK button.

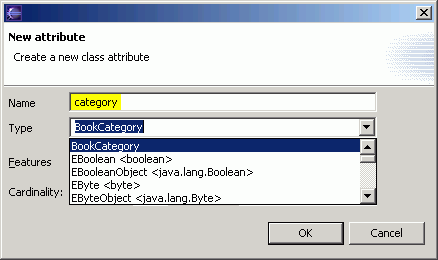
- With the Book class selected, right-click and select New > Attribute, and enter pages as the attribute name. Select EInt as the type and click the OK button.

- With the Book class selected, right-click and select New > Attribute, and enter category as the attribute name. Select BookCategory as the type and click the OK button.
- Now you should have created 4 classes in the library project.

- Save the model by selecting File > Save or simply press the Ctrl+S key.

Step 3: Creating Associations
- In the editor view, click on the Association button
 .
.

- Note that as you move your mouse pointer over a class, the class will change color. Click on the Library class.

- Next, move the mouse pointer over to the Writer class and click on it.

- As soon as you release the mouse button, the association properties dialog comes up.
On the 1st Association End tab, change the name to writers, select the Containment checkbox, and change the upper bound to -1.
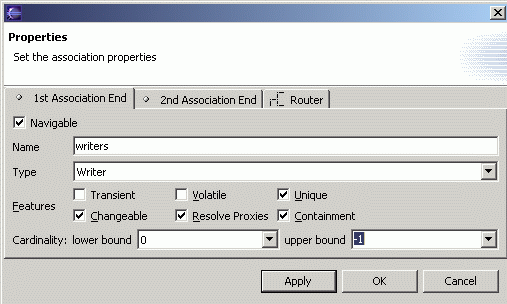
The Containment property indicates that a Library object will contain Writer objects through this writers association. The upper bound of -1 means a Library object can own more than one Writer objet.
- Click on the 2nd Association End tab, and deselect the Navigable checkbox.
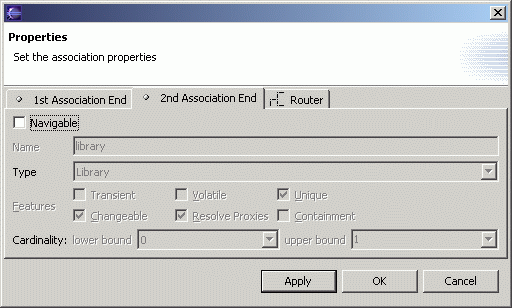
This indicates that from a Writer object, you cannot navigate to the Library object that owns it.
- Click on the Router tab, select the Manual radio button. The selections on this tab do not affect the properties of the association in the ecore model. They only affect how the association line is drawn in the editor. Click the OK button.

- An arrow is now drawn between the Library class and the Writer class. to represent the association we just created

- Now, we are going to create the containment association between Library and Book. It is similar to the association between Library and Writer.
Click on the button and then on the Library class. Then click on the Book class. On the 1st Association End tab of the association properties dialog, change the name to books, select the Containment checkbox and change the upper bound to -1.
button and then on the Library class. Then click on the Book class. On the 1st Association End tab of the association properties dialog, change the name to books, select the Containment checkbox and change the upper bound to -1.

- On the 2nd Association End tab, deselect the Navigable checkbox. On the Router tab, select the Manual radio button. Click the OK button.
- Next we are going to create the association between Book and Writer.
Click on the Association button , then click on the Book class and then click on the Writer class.
, then click on the Book class and then click on the Writer class.

- On the 1st Association End tab, change the name to author. Leave the Containment checkbox unchecked, and change the lower bound to 1. We assume a book will have exactly one author.

- Click on the 2nd Association End tab. Change the name to books and change the upper bound to -1. A writer can author zero or more books.

- Click on the Router tab, select the Manual radio button and click the OK button. The association is drawn in the editor view.

- We can make the class diagram look tidier if we can make the line that represents the association between the Writer and Book classes be drawn so that it appears horizontal and without the jagged edge. This can be done easily in the editor.
Click on the Writer class to select it. Next, holding down the Shift key, click on the Book class to add it to the selection.

- Right-click and select Alignment > Align Middle.

- Now, the diagram looks much neater. Press Ctrl+S key to save the model.

Step 4: Generating the Model and Editor
- In the editor view, right-click on the blank area. Select Generate All.

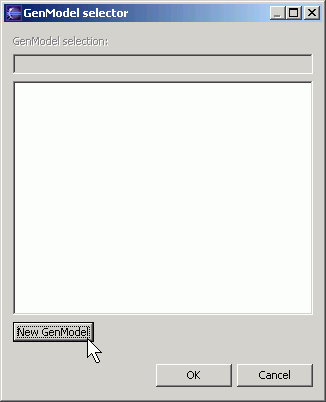
- The first time you do code generation on a project, you will need to create the GenModel model. The GenModel model is auxiliary to the EMF model. It contains information about code generation like the directory into which the code is generated and the adapter pattern.
The GenModel selector will come up. Click on the New GenModel button.
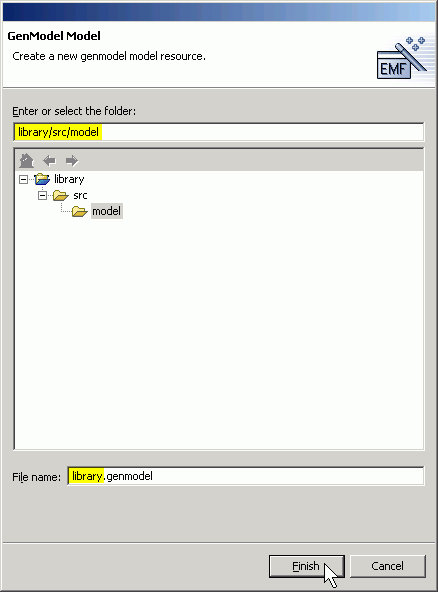
- Expand the library project and select the model folder. Change the file name to library.genmodel. Click the Finish button.
- You are back in the GenModel selector. Click the OK button and code generation begins.

- When the code generation is finished, the GenModel and the EMF model code for the library project will have been generated. In addition, the library.edit and library.editor projects will have been generated and be ready to execute.

- Switch to a Java perspective or a Debug perspective and then follow Step 4 in the tutorial "Generating an EMF Model" to run the generated editor.
Step 5: Modifying the Model
When you modify the EMF model in the graphical editor, it will sychronize the changes with the corresponding GenModel model.
- Working in the Resource perspective, double-click on the library.genmodel in the Navigator view to open it so that both the EMF model and GenModel model are shown. If you have closed the EMF model, double-click on the library.ecore file or the library.ecd file in the Navigator view to open the EMF model.

- Go to the EMF model view, select the Book class, right-click and select New > Attribute to add a new attribute. Enter isbn as the name and click the OK button.

- You can see that the EMF model and the GenModel model are not synchronized. The newly added attribute isbn is not in the GenModel model.

- To synchronize, save the EMF model by selecting File > Save or simply pressing the Ctrl+S key.
- The change still does not show up in the GenModel model yet. You have to switch the GenModel model view into focus. It will then be reloaded. When you expand to the Book class in the GenModel model again, you will find the new attribute.

'IT-Consultant' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 최신 MP3 다운로드 (0) | 2009.10.22 |
|---|---|
| Automatic Shared Memory Management (0) | 2009.10.20 |
| UML을 쉽게 설명한 문서 (0) | 2009.10.12 |
| gwt dnd 버전 호환성 정리 (0) | 2009.10.07 |
| 오라클 11g에서 Orange 3.0이 안된다. (0) | 2009.09.30 |